Seven diatonic scales
Diatonic Scales
The most common scales in popular western music are the major and minor scales. Both of these are diatonic. There are quite a few diatonic scales, and they are all characterised by having seven notes per octave. These notes are divided by five whole steps and two half steps, with the two half steps being separated by at least two whole steps. Take a look at a piano keyboard - if you play every white key from C to C, you will have moved like this: whole step - whole step - half step - whole step - whole step - whole step - half step.
In this article we will take a look at the most common diatonic scales, as well as two alternative diatonic scales.

The Major Scale
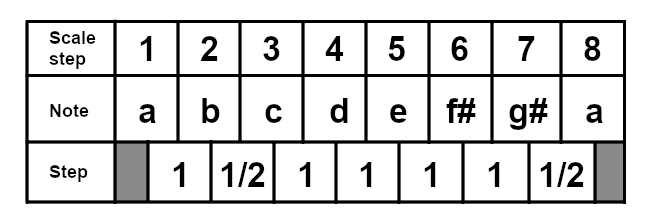
The major scale, also known as the Ionian scale, is one of the most widely used scales in popular music, and is generally thought of as having a "happy" quality. A major scale will always have the same sequence of intervals (steps) between each note of the scale. These will always be (whole steps are 1, half steps are 1/2): 1 - 1 - 1/2 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1/2. Take a look at this C major scale:
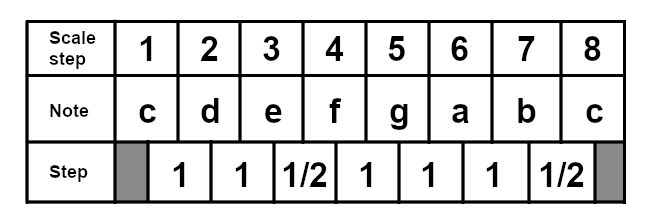
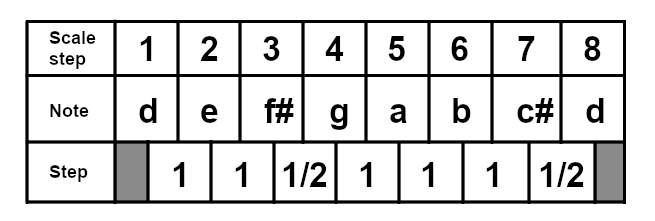
This will always be the sequence of intervals in a major scale. If you wanted to play a D major scale, it would look like this:
The Minor Scales
In this section we will take a look at the natural minor scale, as well as two alternative diatonic scales: The harmonic minor scale and the melodic minor scale. These are both used quite a bit in western music, which is why we're including them here.
The Natural Minor Scale
The minor scale, also known as the Aeolian scale, is arguably as common in western music as the major scale. It is generally thought of as having a "sad" quality. The natural minor scale has the same number of whole step and half step intervals as a major scale, just in a different sequence. For the natural minor scale, the sequence is: 1 - 1/2 - 1 - 1 - 1/2 - 1 - 1.
Take a look at the A minor scale. It is the relative minor of C major, and as such contains the same notes:
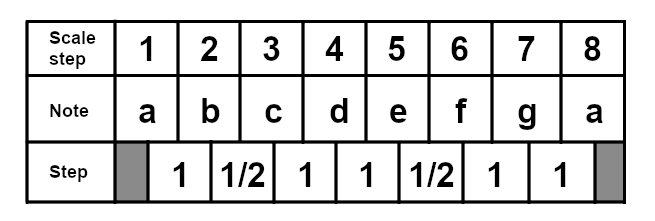
The Harmonic Minor Scale
The Harmonic Minor Scale differs from the natural minor scale by only one note, the raised seventh, giving it three half steps and one "step and a half". This makes it stand apart from the natural minor scale quite a bit, and it has a somewhat "Middle Eastern" quality. The scale has become very popular in certain styles of heavy metal music. The sequence for a harmonic minor scale is: 1 - 1/2 - 1 - 1 - 1/2 - 1 and 1/2 - 1/2.
For reference, here is the A harmonic minor scale:
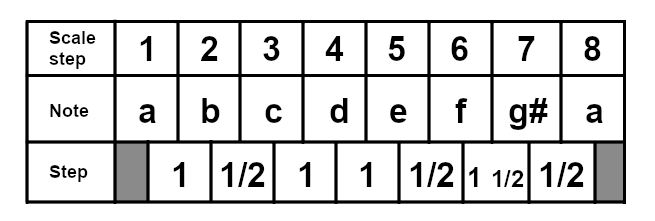
The Melodic Minor Scale
Some composers found the harmonic minor scale difficult to work with, and therefore raised the sixth by one semitone as well. For an example of the melodic minor scale in popular music, listen to "Sorry Seems To Be The Hardest Word" by Elton John. The sequence of intervals for a melodic minor scale is: 1 - 1/2 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1/2. Like a diatonic scale it has five whole steps and two half steps, but they are not distributed evenly as they would be in a diatonic scale.
The Church Modes
If we take the seven notes of the C major scale (All othe white keys on a keyboard) and play them starting on one of the other notes, we will get a different scale, as the sequence of intervals will be different. There is a name for each of these seven scales, and collectively they are known as the church modes. In this section we will present the seven scales as played based on the C major scale, as well as how the key of C would like in this mode.
The Ionian Mode
This is just the major scale, which we've already seen.

The Dorian Mode
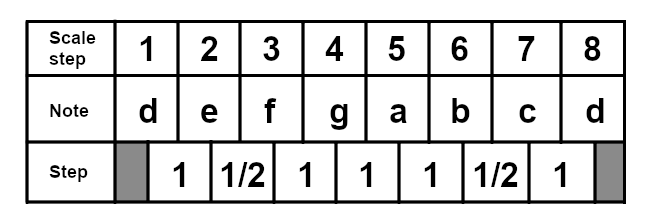
The dorian mode starts on the second degree of the major scale, so in the case of C major, it would start on D. Though not particularly common in popular music, songs like Eleanor Rigby by The Beatles and Mad World by Tears For Fears have used the dorian mode. Here is the D dorian scale:
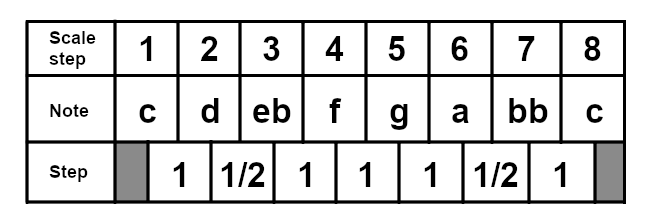
And here is the C dorian scale for reference:
The Phrygian Mode
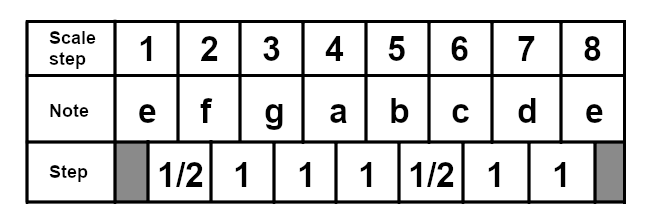
The phrygian mode starts on the third degree of the major scale, so in the case of C major, it would start on E. The phrygian mode is very rare in popular music. Here is the E phrygian scale:
And here is the C phrygian scale for reference:
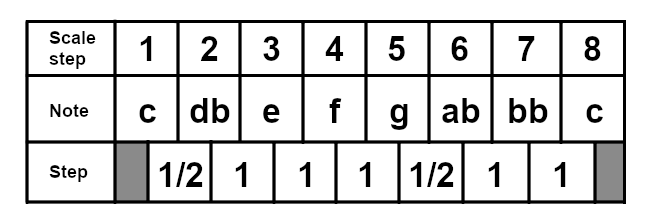
The Lydian Mode
The lydian mode starts on the fourth degree of the major scale, so in the case of C major, it would start on F. The Lydian mode has found its way into a few pieces of popular western music, but perhaps the most popular is its use in the theme song for "The Simpsons". Here is the F lydian scale:
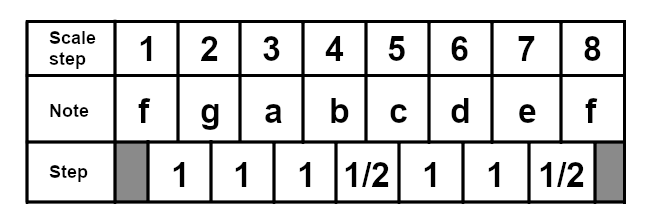
And here is the C lydian scale for reference:
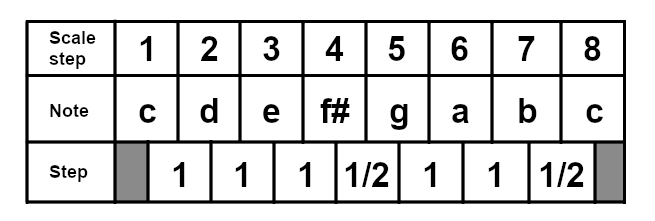
The Mixolydian Mode
The mixolydian mode starts on the fifth degree of the major scale, so in the case of C major it would start on G. The mixolydian mode is arguably the third most popular diatonic scale in western popular music, after major and minor. Songs like Clocks by Coldplay, Royals by Lorde, Express Yourself by Madonna and Sweet Child o' Mine by Guns'n'Roses are all in mixolydian. Here is the G mixolydian scale:
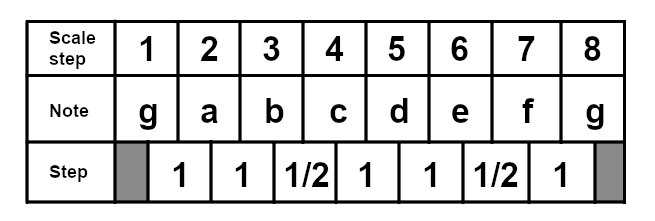
And here is the C mixolydian scale for reference:
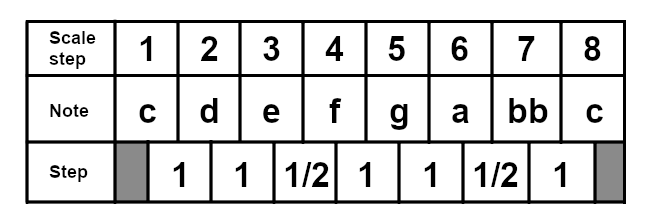
The Aeolian Mode
This is the natural minor scale, which we have already discussed. In the case of C major, it would start on the sixth degree, meaning the A. Here is the A minor scale:

And here is the C minor scale for reference:
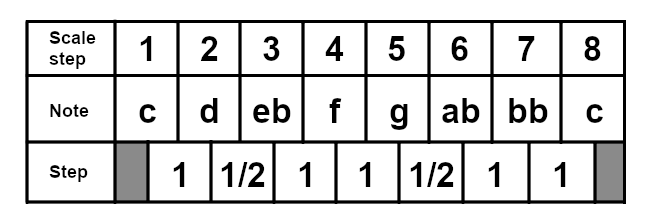
The Locrian Mode
The locrian mode starts of the seventh degree of the major scale, so in the case of C major it would start on B. The locrian mode is the only diatonic scale to contain a tritone interval, making it unsuited for popular music. However, Björk's Army Of Me does contain the locrian mode, and some heavy metal uses it as well. Here is the B locrian scale:
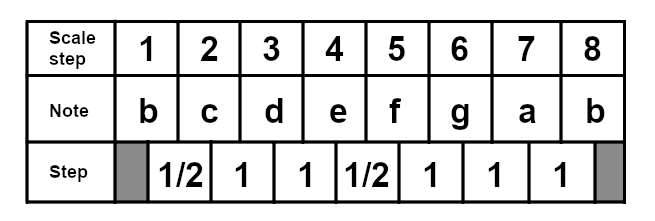
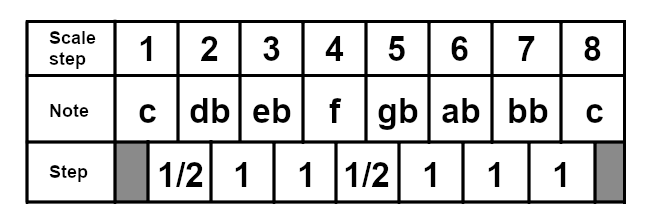
And here is the C locrian scale, for reference:
Want To Learn Music Theory?
Do you want to learn music theory? Maybe you already know, but you want to improve your abilities? We have lots of talented and experienced teachers all over the country. Find a teacher in your city today!
- Music theory teachers in London
- Music theory teachers in Birmingham
- Music theory teachers in Leeds
- Music theory teachers in Liverpool
- Music theory teachers in Manchester
If you thought this article was useful, you might also find the following interesting…
- Learn how to substitute chords in songs to make them more interesting
- Learn the basics of modal harmony - the basis of jazz music!
- Learn the basics of functional harmony
- Learn to analyze blues harmonies using roman numeral analysis
- Learn how to determine which chords to play based on the scale you're playing
- Season Plan - Save 15% on music lessons
Who Are We?
The office team of MusicTutors are all professional musicians and educators. We also believe that we have the best job in the world. We get to spend our day talking to students across the country about how much they love music and we have helped hundreds of people connect with the perfect, professional tutor for them. We'd love to help you too! Please get in touch with us and tell us your story. 07946125613 Or send us a mail to [email protected]. We can't wait to hear from you!
